Understanding Flunarizine and its Effects on Blood Pressure
Flunarizine is a medication that has been around for quite some time. It has various uses, but one of the most important aspects of this drug is its effect on blood pressure. As a blogger who's always interested in learning about health and wellness, I found it important to share what I've learned about Flunarizine and blood pressure. So, let's dive into this topic and explore what you need to know about this medication and its impact on our bodies.
What is Flunarizine and What is its Primary Use?
Flunarizine is a drug that belongs to the group of calcium channel blockers. These medications are primarily used to treat migraine headaches and vertigo. Flunarizine works by preventing the constriction of blood vessels in the brain, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Additionally, it helps with vertigo by improving blood flow to the inner ear, which helps with balance and coordination.
How Does Flunarizine Affect Blood Pressure?
As a calcium channel blocker, Flunarizine can have an impact on blood pressure. The way it works is by inhibiting the movement of calcium ions into the cells of the heart and blood vessels. This action results in the relaxation of blood vessels, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure. However, it's important to note that Flunarizine is not typically prescribed for the primary purpose of treating high blood pressure, and its effect on blood pressure may vary from person to person.
Can Flunarizine Cause Low Blood Pressure?
There is a possibility that Flunarizine can cause low blood pressure (also known as hypotension) in some individuals. This is because the medication can cause blood vessels to relax, which may lead to a decrease in blood pressure. If you are taking Flunarizine and are experiencing symptoms of low blood pressure, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, it is important to consult your healthcare provider immediately.
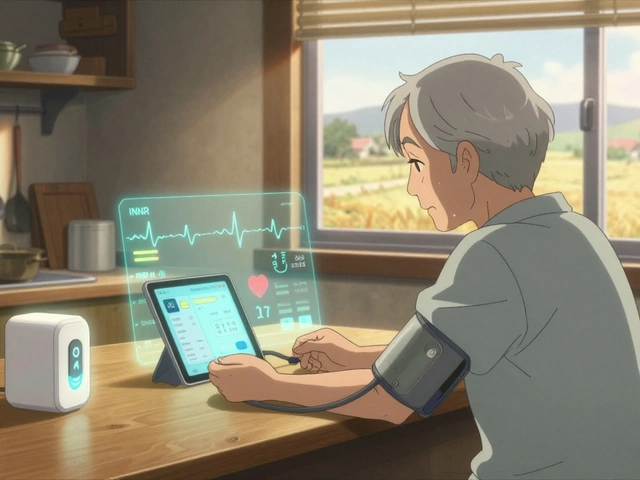
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure While on Flunarizine
While taking Flunarizine, it's important to keep an eye on your blood pressure, especially if you have a history of high or low blood pressure. Regularly monitoring your blood pressure can help you and your healthcare provider identify any potential issues early on and adjust your treatment accordingly. This can be done at home with a blood pressure monitor or during routine check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects of Flunarizine
Like any medication, Flunarizine can have potential side effects. Some common side effects include drowsiness, weight gain, nausea, and dry mouth. More serious side effects can include depression, extrapyramidal symptoms (such as tremors or involuntary muscle movements), and an irregular heartbeat. If you experience any concerning side effects while taking Flunarizine, it's important to consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Interactions with Other Medications
When taking Flunarizine, it's crucial to be aware of possible interactions with other medications. Some drugs that may interact with Flunarizine include other calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, and certain antidepressants. These interactions can potentially lead to increased side effects or a reduced effectiveness of either medication. Be sure to discuss your current medications with your healthcare provider before starting Flunarizine to avoid any potential complications.
Contraindications for Flunarizine Use
There are certain situations in which Flunarizine may not be recommended or should be used with caution. Individuals with a history of depression, Parkinson's disease, or other movement disorders may need to avoid Flunarizine, as it can potentially worsen these conditions. Additionally, pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using Flunarizine, as its safety during pregnancy and lactation has not been fully established.
Flunarizine Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Flunarizine can vary depending on the individual and the specific condition being treated. It's important to follow your healthcare provider's instructions when taking Flunarizine to ensure you're receiving the appropriate dosage for your needs. Typically, Flunarizine is taken once daily, but your healthcare provider may adjust your dosage as needed.
Final Thoughts on Flunarizine and Blood Pressure
In conclusion, Flunarizine is a medication that can have an impact on blood pressure, but its primary use is for the treatment of migraine headaches and vertigo. While it's not typically prescribed for the sole purpose of managing blood pressure, it's important to monitor your blood pressure while taking Flunarizine and to be aware of potential side effects and interactions with other medications. As always, consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medication or if you have concerns about your blood pressure while taking Flunarizine.








Comments
Keeping an eye on your numbers is a good habit, especially when you start a new drug. Flunarizine’s calming effect on vessels can dip your pressure a bit, so a simple home monitor can save you a lot of worry. It’s also helpful to log any dizzy spells and share them with your doc – they’ll know if the dose needs tweaking. Remember, being proactive is half the battle won.
OMG, this med can literally make you feel like you’re floatin’ on a cloud, but then bam – you’re wobblin’ around like a newborn giraffe. The drop in pressure? Yeah, it’s real, but don’t freak out; most peeps just feel a lil drowsy. If you’re gettin’ light‑headed, grab a snack and take a breather. Trust me, it’s not the end of the world, but keep tabs on that cuff!
The blood pressure impact is minimal, in my experience.
Flunarizine is a useful tool for migraine prevention, but its vascular effects shouldn't be overlooked.
When the drug relaxes smooth muscle in the arterial walls, systolic and diastolic numbers can drift downward.
This shift is usually modest, yet in patients prone to hypotension it can tip the balance toward dizziness or fainting.
The first step is establishing a baseline reading before you start therapy, ideally taken at the same time of day for consistency.
After you begin the medication, repeat the measurement after a week and then again after a month to spot any trends.
If you notice a steady decline of more than ten millimetres of mercury, bring it up with your physician promptly.
Many clinicians will suggest pairing flunarizine with a low‑dose antihypertensive only if your blood pressure spikes, but that’s rare.
Lifestyle adjustments-adequate hydration, moderate salt intake, and avoiding sudden position changes-can also cushion the drop.
It’s important to be aware of drug‑drug interactions; combining flunarizine with other calcium channel blockers or beta‑blockers can amplify the vasodilatory effect.
Over‑the‑counter supplements like ginkgo or high‑dose vitamin D aren’t usually a problem, but always double‑check with your pharmacist.
Side‑effects such as drowsiness or weight gain usually manifest early, while extrapyramidal symptoms may appear later and warrant immediate medical attention.
For patients with a history of depression or Parkinsonian features, the risk‑benefit calculus shifts, and alternative migraine prophylactics might be preferable.
Pregnant or nursing individuals should discuss the limited safety data with their obstetrician before making a decision.
In practice, most people tolerate flunarizine well and only need occasional blood pressure checks, especially after dose adjustments.
Bottom line: stay vigilant, keep a simple log, communicate openly with your health‑care team, and you’ll likely reap the migraine‑relief benefits without major cardiovascular surprises.
It’s commendable that you’re taking charge of your health by tracking blood pressure while on flunarizine. The medication’s calcium‑channel blocking properties can indeed cause modest reductions, which are generally well tolerated. Should you experience any syncopal episodes or persistent light‑headedness, a prompt consultation is advisable. Meanwhile, maintaining regular exercise and a balanced diet will further support vascular stability.
By the way, the pharmacokinetic profile of flunarizine includes a half‑life of roughly 19 days, which means steady‑state concentrations build up slowly; monitoring should therefore extend beyond the initial weeks 😊. Additionally, clinicians often recommend a gradual titration to mitigate abrupt hypotensive dips.
While your anecdotal advice is appreciated, it neglects the nuanced interplay between cytochrome P450 isoforms and flunarizine metabolism, a factor that fundamentally dictates inter‑individual variability in hemodynamic response. A rigorous understanding of these enzymatic pathways is indispensable for any substantive discourse.
Stop overcomplicating a simple issue with obscure enzyme talk; most patients just need clear guidance, not a lecture on metabolic pathways.