Antiparasitic Drugs: What They Are and Why They Matter
When dealing with antiparasitic drugs, medicines designed to eliminate or control parasites that invade humans or animals. Also known as anthelmintics, they are essential for keeping communities healthy. antiparasitic drugs work across a wide range of parasites, from tiny protozoa that cause malaria to larger helminths that cause intestinal worm infections.
Core categories and how they fit together
Antiparasitic drugs encompass two major families: anthelmintics, agents that target roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes and antiprotozoal agents, compounds that act against single‑cell parasites such as Plasmodium, Giardia, and Trichomonas. A typical treatment plan might combine an anthelmintic like albendazole for hookworm with an antiprotozoal like metronidazole for giardiasis, showing how the two sub‑categories complement each other.
These drugs are chosen based on the specific parasitic infection, the disease caused by a worm, protozoan, or ectoparasite and its life cycle stage. Knowing the parasite’s biology is crucial because many drugs only affect certain stages; for example, ivermectin is highly effective against the larval forms of onchocerciasis but less so against adult filarial worms.
Effective therapy requires proper diagnosis and the right drug dosage. Health professionals often rely on stool microscopy, blood smears, or rapid antigen tests to confirm the infection. Once confirmed, they consider factors such as patient age, weight, pregnancy status, and potential drug interactions before prescribing the appropriate antiparasitic regimen.
One challenge that keeps clinicians on their toes is drug resistance, the ability of parasites to survive treatments that once worked. Resistance has risen in malaria parasites against artemisinin and in intestinal worms against benzimidazoles. This pushes researchers to develop new compounds, rotate drug classes, and combine therapies to stay ahead of evolving parasites.
The landscape of antiparasitic drugs also connects to broader public‑health efforts such as mass drug administration (MDA) programs, vector control, and sanitation improvements. By bundling medication distribution with education about hygiene and safe water, communities can cut infection rates dramatically. The synergy between medication and preventive measures illustrates why antiparasitic drugs are just one piece of a larger health puzzle.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dig deeper into specific drugs, compare treatment options, and offer practical advice on safe usage. Whether you’re a patient looking for clear guidance or a professional seeking up‑to‑date comparisons, the collection ahead covers the most relevant topics around antiparasitic drugs.
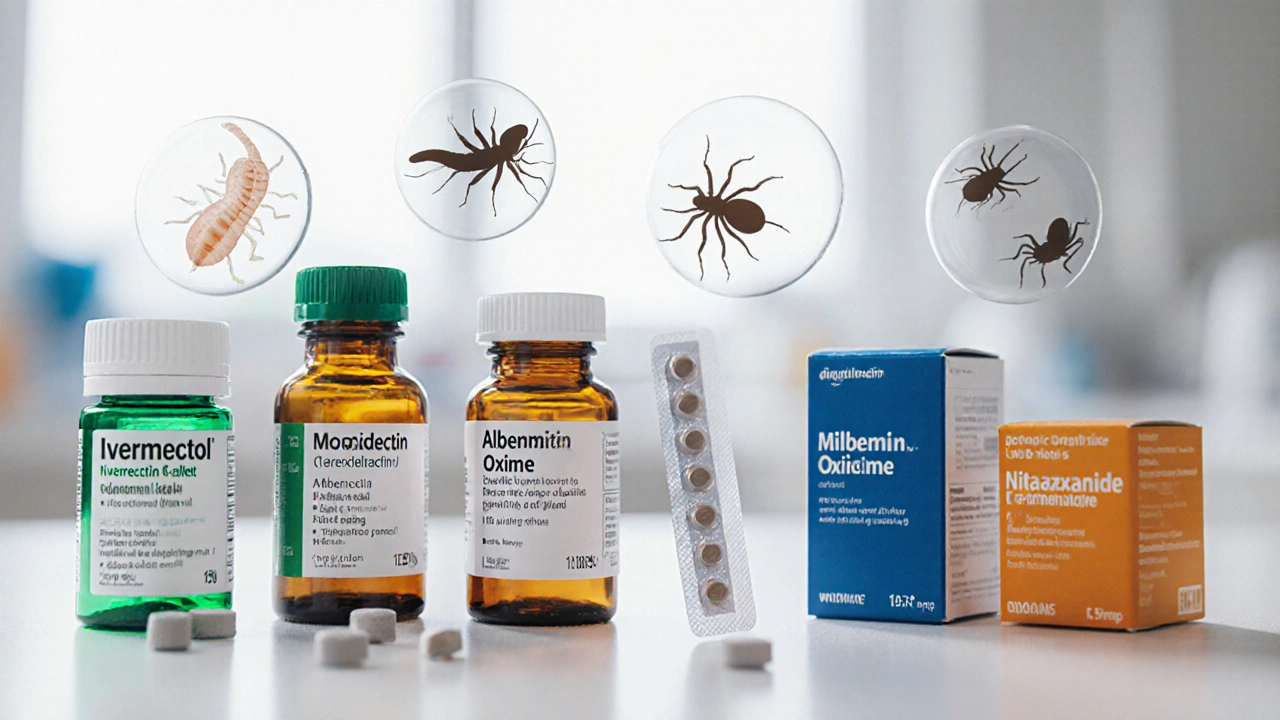
A detailed side‑by‑side look at Ivermectol versus Moxidectin, Albendazole, Milbemycin oxime, and Nitazoxanide, covering efficacy, safety, dosing, cost, and when each drug is the right choice.
Read more