Postpartum Depression: Signs, Causes, and Treatment Options
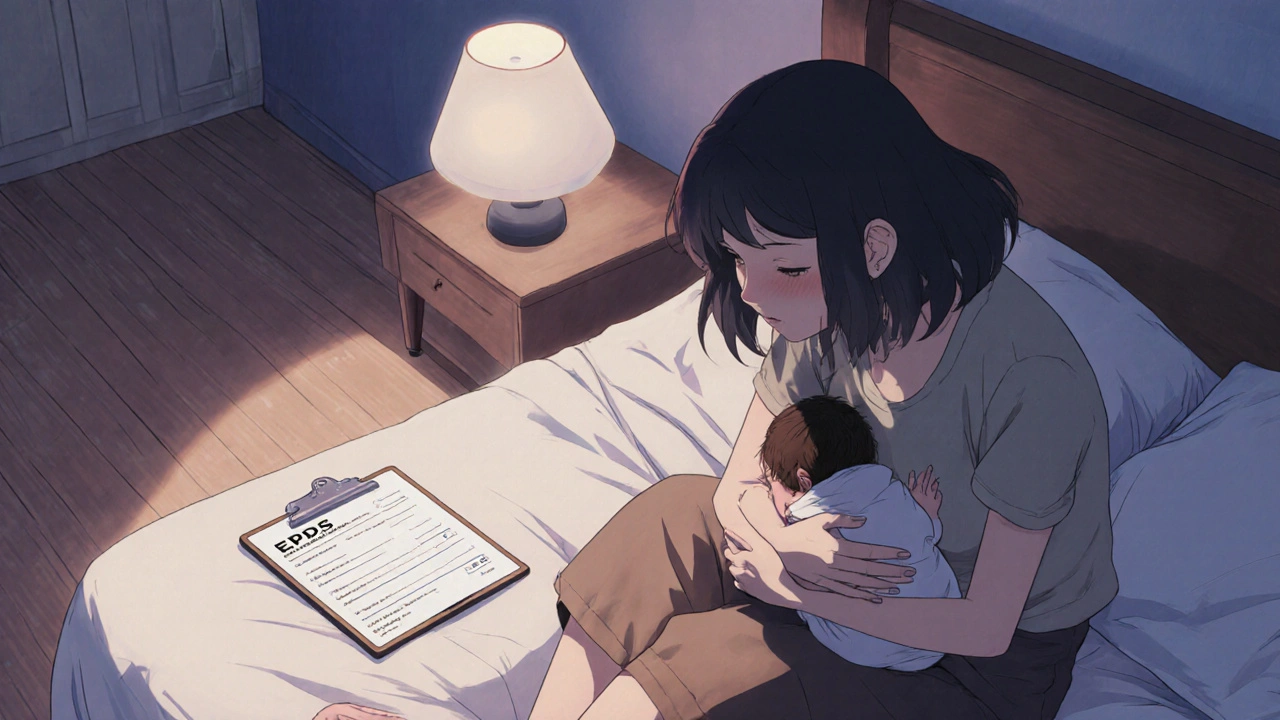
When dealing with postpartum depression, a mood disorder that can affect new mothers after childbirth, also known as postnatal depression, it’s often linked to maternal anxiety, persistent worry that can arise during the early weeks and sleep disturbance, broken sleep patterns common after delivery. In short, postpartum depression encompasses emotional, hormonal, and lifestyle factors that together shape a mother’s wellbeing.
One of the first things to notice is the hormonal roller‑coaster that happens after birth. Levels of estrogen and progesterone drop sharply, and that shift can trigger mood swings. At the same time, the body releases cortisol, the stress hormone, which can amplify anxiety and make sleep even harder to catch. This hormone‑stress link means that cortisol spikes, often seen in new mothers stressed by newborn care directly influence the severity of postpartum depression. Understanding this connection helps you see why a simple “just relax” tip often falls flat – the body is physically primed for mood changes.
Key Factors and Management Strategies
Beyond hormones, practical issues play a big role. Breastfeeding, for instance, can be a source of both comfort and frustration. Difficulty latching or low milk supply adds pressure, and that pressure fuels anxiety. When anxiety rises, sleep disturbance worsens, creating a feedback loop that deepens depressive symptoms. Breaking that loop usually starts with two simple steps: establishing a sleep‑support plan and seeking professional help early. A sleep‑support plan might include short daytime naps, sharing night‑time feeds with a partner, or using white‑noise machines to create a calmer environment.
Professional support can take many forms. Cognitive‑behavioral therapy (CBT) is a proven method for tackling the negative thought patterns that keep postpartum depression alive. Medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), is another option, especially when symptoms are moderate to severe. It’s important to remember that medication safety is evaluated carefully for nursing mothers, and many doctors consider certain SSRIs safe while breastfeeding. The choice between therapy, medication, or a combo depends on individual circumstances, severity of symptoms, and personal preferences.
Social support is the third pillar often overlooked. Having a partner, family member, or friend who can lend a hand with chores, meals, or baby care can dramatically reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed. Support groups—online or in‑person—also provide a space to share experiences, learn coping tools, and feel less isolated. When you hear other moms talk about similar struggles, it normalizes the experience and makes it easier to ask for help.
Nutrition plays a subtle but real part, too. Foods rich in omega‑3 fatty acids, B‑vitamins, and iron support brain chemistry and energy levels. Skipping meals because of a newborn’s schedule can worsen fatigue and irritability, so planning quick, nutrient‑dense snacks is a small habit that adds up. Hydration matters as well; dehydration can mimic anxiety symptoms and make concentration harder.
Finally, it’s worth noting that not every mood dip after birth turns into postpartum depression. The DSM‑5 defines postpartum depression as a persistent low mood lasting at least two weeks, accompanied by loss of interest, changes in appetite, feelings of guilt, or thoughts of harming oneself. If you or someone you know shows these signs, reaching out to a healthcare provider promptly is crucial. Early intervention can prevent the condition from deepening and make recovery faster.
Below you’ll find a curated collection of articles that dive deeper into each of these areas—hormonal changes, anxiety management, sleep strategies, medication guidance, and real‑world tips from caregivers. Browse the posts to get actionable insights you can start using today, and remember that help is just a conversation away.