Systemic Antifungals: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When a fungal infection goes deep—beyond your skin or nails—it needs systemic antifungals, oral or intravenous medications that travel through your bloodstream to kill fungi inside your body. Also known as oral antifungals, these drugs don’t just sit on the surface. They reach your lungs, liver, even your bloodstream to fight infections that topical creams can’t touch. Unlike antifungal shampoos or creams, systemic antifungals are prescribed for serious cases like invasive candidiasis, histoplasmosis, or fungal pneumonia—conditions that can turn dangerous if left untreated.
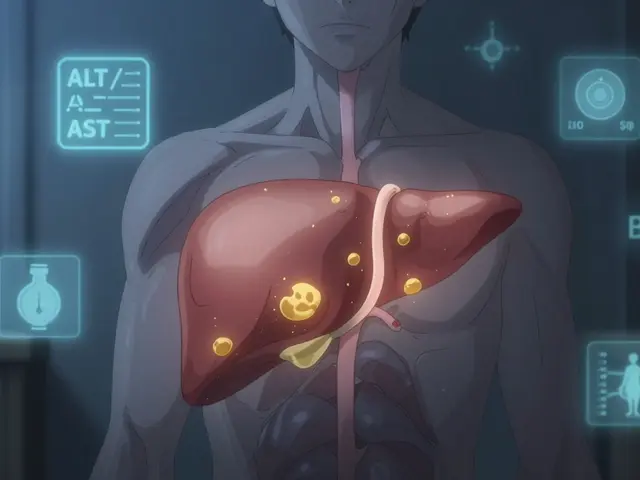
These medications don’t come without trade-offs. antifungal side effects, ranging from nausea and headaches to liver damage and dangerous drug interactions are common. That’s why they’re not handed out lightly. Many patients on systemic antifungals, especially those taking fluconazole, itraconazole, or voriconazole also need regular blood tests to check liver function. Some interact badly with blood thinners like warfarin, which is why you’ll often see these drugs mentioned together in pharmacy guides. And if you’re on other meds—like statins, antidepressants, or even over-the-counter supplements—your pharmacist needs to know. A simple mix can raise your risk of toxicity or make the antifungal useless.
What you won’t find in most doctor’s office brochures is how often people misjudge these infections. Many assume a stubborn rash or nail change is just ‘bad hygiene’ and delay treatment—until the fungus spreads. Others stop taking the drug too soon because they feel better, not realizing fungi can hide in tissues and come back stronger. That’s why pharmacy counseling often focuses on adherence, not just dosing. The right systemic antifungal depends on the infection type, your liver health, and what other drugs you’re taking. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides from pharmacists and patients who’ve walked this path. You’ll see how people manage side effects, avoid dangerous interactions, and recognize when a fungal infection is more than just a nuisance. Whether you’re starting treatment, worried about a reaction, or just trying to understand why your doctor ordered blood work, these posts give you the clarity you need—no jargon, no fluff, just what works.
Systemic antifungals like ketoconazole and posaconazole can dangerously increase statin levels, raising the risk of muscle damage and kidney failure. Learn which combinations to avoid and safer alternatives.
Read more