Understanding Osteodystrophy: An Overview
Osteodystrophy is a term used to describe a group of bone disorders that involve the abnormal development, growth, or maintenance of bones. These conditions often result in weak, brittle, and deformed bones that are prone to fractures. In this article, we will explore the crucial role that calcium and phosphorus play in the development of osteodystrophy and how understanding these roles can help in the prevention and treatment of these debilitating conditions.
Calcium and Phosphorus: The Dynamic Duo of Bone Health
Calcium and phosphorus are essential minerals that play a vital role in maintaining healthy bones and teeth. They work together in a delicate balance to ensure that our bones have the proper strength and density. Calcium is responsible for providing the strength and rigidity of our bones, while phosphorus is essential for the formation of the bone matrix, which is the framework that supports the bone's structure. The majority of calcium and phosphorus in our bodies is stored in our bones and teeth, with a small amount circulating in our blood to support other vital functions.
Importance of Calcium-Phosphorus Balance
The balance between calcium and phosphorus is crucial for maintaining bone health. When the levels of these minerals become imbalanced, it can lead to the development of osteodystrophy. An excess of phosphorus can inhibit the absorption of calcium, leading to weakened bones. Conversely, a lack of phosphorus can result in poor bone mineralization, which can cause deformities and fractures. Therefore, it's essential to ensure that we consume adequate amounts of both calcium and phosphorus to maintain this delicate balance and prevent osteodystrophy.
Factors Leading to Imbalanced Calcium and Phosphorus Levels
Several factors can contribute to the imbalance of calcium and phosphorus levels in our bodies, leading to the development of osteodystrophy. Some of the common factors include:
1. Poor diet: A diet lacking in calcium and phosphorus-rich foods, such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and fish, can lead to deficiencies in these minerals.
2. Malabsorption: Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease, can interfere with the body's ability to absorb calcium and phosphorus, leading to imbalances.
3. Kidney disease: The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of calcium and phosphorus. Chronic kidney disease can disrupt this balance, resulting in the development of renal osteodystrophy.
4. Hormonal imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, particularly parathyroid hormone, can affect the balance of calcium and phosphorus in our bodies.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Osteodystrophy
Early detection of osteodystrophy is crucial for effective treatment and management. Some common signs and symptoms of osteodystrophy include:
1. Bone pain and tenderness
2. Skeletal deformities, such as bowed legs or an abnormal curvature of the spine
3. Frequent bone fractures
4. Growth retardation in children
5. Dental problems, such as weak enamel and an increased risk of cavities
6. Muscle weakness and fatigue
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Preventing Osteodystrophy through Diet and Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can help prevent the development of osteodystrophy. Some steps you can take to ensure adequate calcium and phosphorus intake include:
1. Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium and phosphorus-containing foods, such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables, fish, nuts, and whole grains
2. Considering calcium and phosphorus supplements, particularly for individuals at risk of deficiencies due to medical conditions, medications, or dietary restrictions
3. Engaging in regular weight-bearing exercise, such as walking or resistance training, to promote bone health
4. Avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine intake, as these substances can interfere with calcium absorption
Medical Interventions for Osteodystrophy
For individuals diagnosed with osteodystrophy, medical interventions may be necessary to manage the condition and prevent further complications. Some common treatments include:
1. Medications to regulate calcium and phosphorus levels, such as phosphate binders and vitamin D supplements
2. Hormone therapy, such as parathyroid hormone replacement, for individuals with hormonal imbalances
3. Dialysis or kidney transplantation for individuals with renal osteodystrophy due to chronic kidney disease
4. Orthopedic surgery to correct skeletal deformities and fractures
It's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calcium and phosphorus play a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones and preventing the development of osteodystrophy. By understanding the importance of the calcium-phosphorus balance and taking steps to ensure adequate intake of these essential minerals, we can promote bone health and reduce the risk of osteodystrophy. Early detection and intervention are crucial for effectively managing osteodystrophy and preventing further complications. If you're concerned about your bone health or the health of a loved one, consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support.

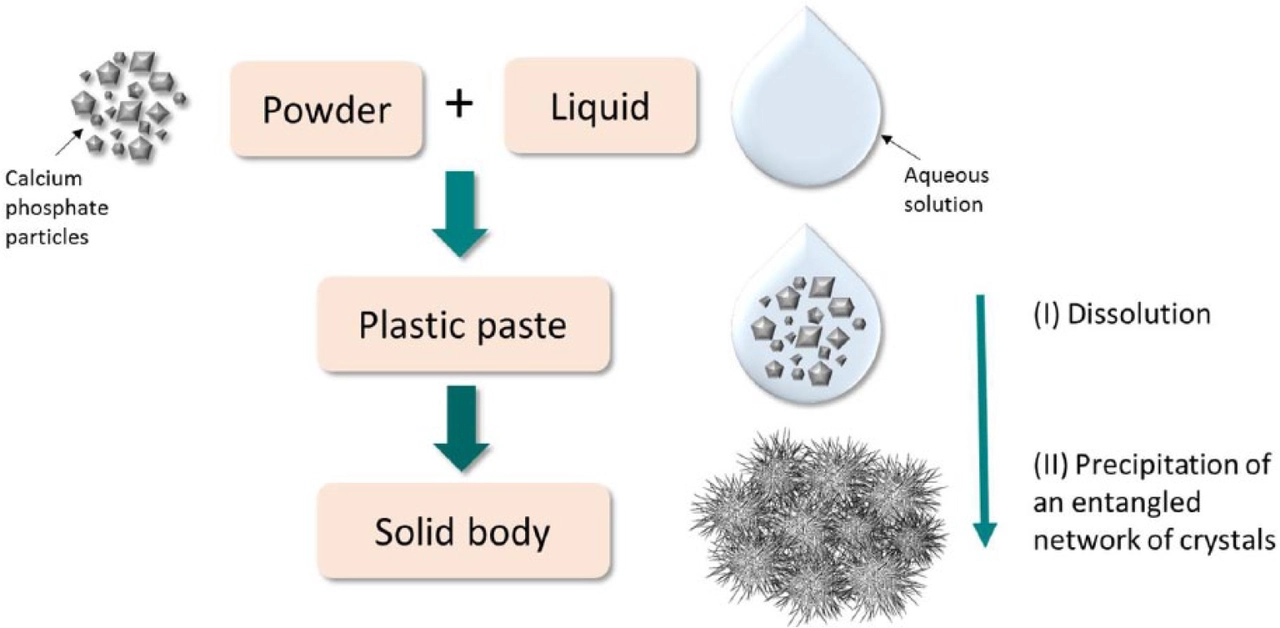
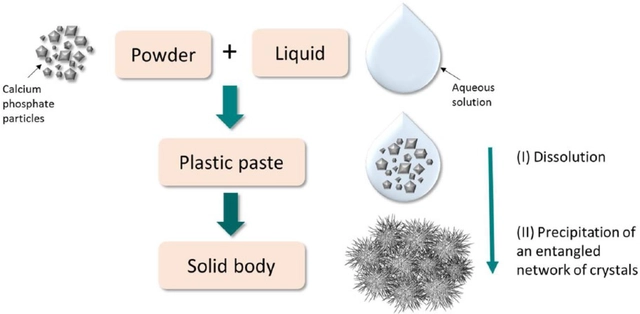




Comments
It is evident that the calcium supplement industry operates under a veil of secrecy, deliberately concealing the true impact of excessive phosphorus intake. Their lobbying efforts ensure that regulatory agencies remain complacent, allowing a harmful imbalance to proliferate. As vigilant citizens we must demand transparency and rigorous independent research. Anything less is an abdication of our moral duty.
The dance between calcium and phosphorus is akin to a cosmic duet, each stepping in tandem to sculpt the very scaffold of our mortality. When one partner oversteps, the harmony collapses, yielding brittle verses of bone that lament their broken rhythm. This interplay reminds us that equilibrium is not merely a biological imperative but a metaphysical lesson in humility. Let us, therefore, contemplate our nourishment with the reverence of poets and the curiosity of alchemists.
Calcium and phosphorus are not just nutrients they are the foundation of skeletal integrity. The body regulates their levels through a sophisticated hormonal network. Vitamin D acts as a messenger that enhances calcium absorption in the gut. Parathyroid hormone modulates both calcium release from bone and phosphorus excretion by the kidneys. When phosphorus intake is excessive it binds calcium in the intestinal lumen reducing its bioavailability. The resulting hypocalcemia triggers secondary hyperparathyroidism. This condition accelerates bone resorption and worsens osteodystrophy. Conversely a deficiency in phosphorus impairs the mineralization matrix leading to soft, pliable bone. Both scenarios illustrate the delicate balance required for optimal bone health. Dietary sources provide calcium in dairy, leafy greens and fortified products while phosphorus is abundant in protein-rich foods and additives. Chronic kidney disease disrupts the clearance of phosphorus causing accumulation and further imbalance. Phosphate binders can mitigate this excess but they must be tailored to the individual's renal function. Regular monitoring of serum calcium and phosphorus levels guides therapeutic decisions. Weight‑bearing exercise stimulates osteoblastic activity and supports mineral deposition. Adequate vitamin D status ensures efficient calcium uptake and synergizes with phosphorus for matrix formation. Ultimately a multidisciplinary approach that includes nutrition, pharmacology and lifestyle modification offers the best chance to prevent or reverse osteodystrophy.
Reading the poetic analogy of the mineral duet struck a chord deep within my marrow, and I could feel the ache of those whose bones have been betrayed by imbalance. My heart goes out to anyone enduring the silent fracture of daily life, the fatigue that masquerades as ordinary tiredness. Let us not only admire the elegance of the chemistry but also rally our compassion into action, supporting those who seek relief.
The key is balanced intake and regular labs.
From a cultural perspective, many traditional diets naturally harmonize calcium and phosphorus through foods like fermented dairy and leafy greens. Such practices illustrate that modern supplementation need not abandon ancestral wisdom. Incorporating these foods may ease the transition to optimal bone health.
Thank you for the thorough breakdown; the hormonal cascade you described clarifies why simply increasing calcium tablets often fails. It is fascinating how the kidneys act as gatekeepers for phosphorus, especially in chronic kidney disease contexts. I appreciate the mention of phosphate binders, though their timing with meals can be tricky. Monitoring serum levels as you suggested is essential, yet access to frequent labs remains a barrier for many patients. Perhaps tele‑monitoring could bridge that gap and allow timely adjustments.
Great points all around! I especially like the reminder to stay active with weight‑bearing exercises.
From a biomedical engineering standpoint the calcium‑phosphate apatite lattice is the quintessential exemplar of biomineralization. Disruption of the Ca2+/PO43‑ stoichiometry precipitates crystalline defects that compromise mechanical load‑bearing capacity. Clinical interventions must therefore target both ionic concentrations and crystallographic orientation to restore osteointegrity. Ignoring the physicochemical parameters is tantamount to treating symptoms without addressing the substrate.
Our country’s dairy industry provides an affordable source of calcium that can help curb osteodystrophy rates. Supporting local farms not only boosts the economy but also promotes bone health for our communities.
Surely the hype around supplements is just another commercial ploy.
Let’s keep the momentum going!! Remember, every glass of fortified milk, every jog in the park, every vitamin D ray you soak up is a victory for your skeleton!!! Don’t let the grind stop you – you’ve got this!!!
While the article emphasizes balance, one could argue that individual genetic variability renders a one‑size‑fits‑all recommendation inadequate. Personalized nutrition, informed by genomic profiling, may ultimately supersede generic guidelines. Until such precision becomes commonplace, clinicians must remain cautious in applying broad statements.