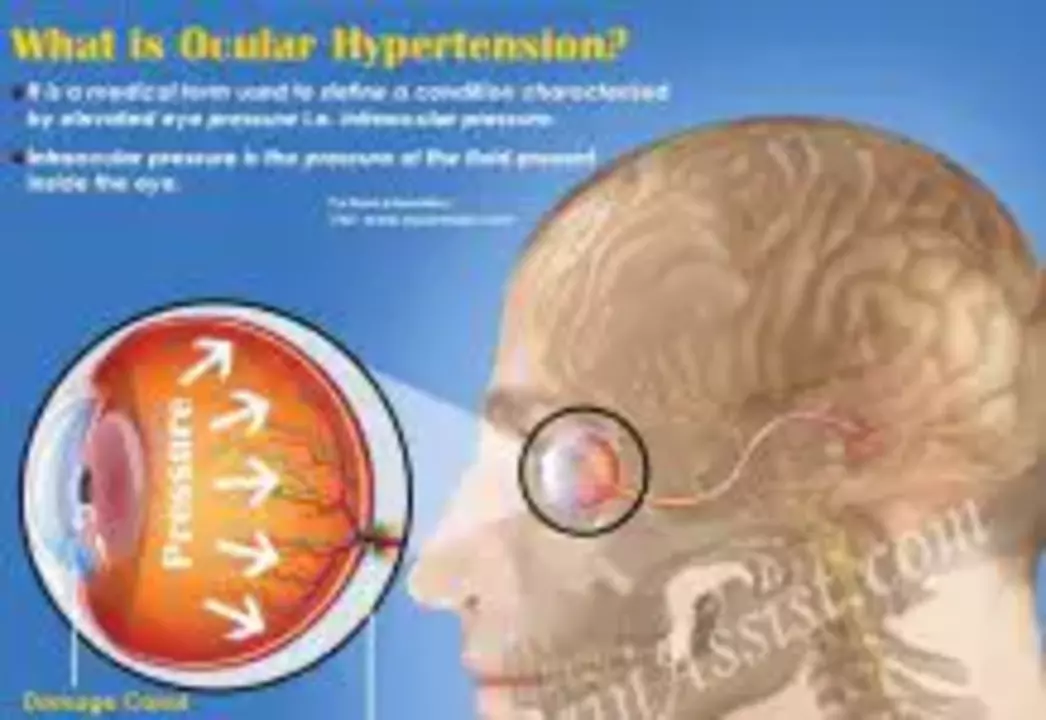
Eye Care: What to Know About Ocular Hypertension and Uveitic Glaucoma
Eye pressure problems can sneak up without pain. If you're worried about glaucoma or raised intraocular pressure, clear steps and the right medicines make a big difference. This page pulls together practical info about common treatments, how they work, and simple tips to protect your vision.
Top treatments to know
Brinzolamide is an eye drop that lowers eye pressure by slowing fluid production inside the eye. People use it for ocular hypertension to reduce the risk of optic nerve damage. Drops are usually applied twice or three times daily as your doctor prescribes. Expect mild burning or a bitter taste at first; serious reactions are rare but should be reported.
Latanoprost helps fluid drain out of the eye, lowering pressure a different way. It's often the first choice for long-term treatment because a single nightly drop can be effective. Watch for eyelash growth, darkening of the iris, or mild eye irritation - these are common and usually harmless, but check with your doctor if they worry you.
Sometimes doctors combine medications when one drug isn't enough. Fixed-combination drops can simplify schedules and reduce how many separate bottles you use. Your eye doctor will pick options based on your pressure readings, eye health, and any other medical conditions you have.
Daily care and follow-up
Use drops exactly as prescribed. Skipping doses or doubling up can reduce effectiveness or cause side effects. A handy tip: put drops in before other ointments or contacts - wait at least ten minutes between different treatments. If you wear contact lenses, remove them before most medicated drops and wait before putting lenses back in unless your doctor says it's okay.
Regular checkups matter. Eye pressure can change without symptoms, so stick to scheduled visits for IOP measurements and optic nerve checks. If your vision blurs, you get eye pain, or see halos around lights, contact your eye care provider quickly - those can signal rising pressure or other problems.
Lifestyle changes help too. Keep blood pressure and blood sugar controlled, avoid smoking, and stay active. Simple eye-friendly habits - wear sunglasses, take breaks from screens, and use proper lighting - reduce strain and support long-term eye health.
Quick how-to for eye drops and storage: Wash your hands and tilt your head back. Pull the lower lid down to make a pocket, squeeze one drop into that pocket, then close your eye and press the inner corner for 1-2 minutes to cut down on taste and systemic absorption. Wait ten minutes before another drop. Keep bottles in original box; some need refrigeration after opening, others do not - check the label. Replace bottles after the time your pharmacist gives, often 28 days, to lower infection risk. If you miss a dose, use it as soon as you remember but don't double the next dose.
If you have questions about brinzolamide, latanoprost, or combining treatments, ask your pharmacist or ophthalmologist for practical advice tailored to your situation. Treatment plans work best when you understand how and why they help.
As a blogger who's passionate about eye health, I've recently come across the significant role brinzolamide plays in treating ocular hypertension. This medication, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, has proven effective in reducing intraocular pressure by decreasing the production of aqueous humor. The ease of administering it as eye drops makes it a convenient option for patients. Moreover, it's often combined with other medications for optimal results. Overall, brinzolamide is an essential treatment for managing ocular hypertension and preventing further complications like glaucoma.
Read more
As a blogger, I've recently come across an interesting topic that I'd like to share with you all - The Role of Latanoprost in the Treatment of Uveitic Glaucoma. Latanoprost is a medication that has been proven to be quite effective in lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients suffering from this condition. It works by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor, which in turn helps regulate eye pressure. However, it's important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone, as some patients may experience side effects such as eye irritation or changes in eye color. Overall, Latanoprost has shown promising results in the management of uveitic glaucoma, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
Read more